Video editing involves much more than just cutting and arranging clips. This is a dynamic and creative process which transforms raw footage into compelling visual narratives.
Each edit brings your vision to life. This allows viewers to experience your creativity on a personal level.
With the best Linux video editing software, creators are transforming their approach to post-production. Without the need to purchase expensive licenses, you can produce stunning videos.
Linux offers a wide range of powerful, free, and open-source software options. Each of these options provides solutions for every level of skill.
Beginners just getting started as well as seasoned professionals seeking advanced tools can find the tools they need at their website. Due to its exceptional flexibility, robust security, and renowned stability, it has achieved this status.
You will discover the best Linux video editing software available today in this article. We will walk you through the process of installing each tool.
We will also provide a brief description of the unique features of each tool. As a final step, we will assist you in choosing the editor that is most appropriate for your creative requirements.
Due to an ever-growing community and regular software enhancements, Linux video editors are now competitive with their Windows and macOS counterparts. Their creative potential is limitless.
Best Linux Video Editing Software
Why Linux is a Game Changer in Video Editing
Linux video editing software has revolutionized the creative landscape by providing unparalleled customization and flexibility.
Unlike traditional proprietary systems that often come with hefty price tags, Linux tools are freely available. They are continuously improved by vibrant, passionate communities.
With this open-source approach, users have access to the latest editing capabilities without incurring any financial burden.
You can rest assured that your creative projects will be protected by Linux’s outstanding stability and security. Even when editing intensively, they operate smoothly. Furthermore, there are many free resources available online.
A comprehensive support community facilitates troubleshooting as well as the learning of new skills.
Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional filmmaker, Linux provides a reliable, innovative, and cost-effective solution.
In terms of video editing, it is a game changer due to its ability to adapt to your evolving creative needs.
Top Linux Video Editing Software Options
Below, we explore the most popular Linux video editing software. Each section includes an in-depth overview, detailed feature lists, pros and cons, installation instructions, and recommendations for who will benefit most from each tool.
1. Kdenlive
Kdenlive is a feature-rich, open-source video editor. It is designed for both beginners and advanced users.
Its user-friendly interface is combined with powerful functionalities. This makes it a top choice for Linux video editing.
Kdenlive supports multi-track editing. You can work with numerous video and audio layers simultaneously.
It has an extensive range of built-in effects, transitions, and color correction tools. You can achieve professional-grade results with these tools.
The software’s modular design lets you customize the workspace. You can match the workspace to your editing style.
Kdenlive is highly adaptable to various projects. It receives continuous updates driven by an active community.
Kdenlive remains at the forefront of Linux video editors. Its proxy editing feature enables smoother performance on older hardware. High-resolution editing is accessible to a broader audience.
Whether you are editing a short film, a YouTube video, or a complex documentary, Kdenlive offers the versatility you need. It is reliable and helps bring your creative vision to life.
Kdenlive Features
- Multi-track Editing: You can manage multiple layers of video and audio.
- Built-in Effects & Transitions: Enhance your projects with creative visual tools.
- Customizable Interface: Tailor the workspace to your unique workflow.
- Proxy Editing: Optimize performance on older systems.
- Wide Format Support: Import and export a vast range of video formats.
Kdenlive Pros and cons
- Pros:
- It is free and open source.
- It has a robust feature set suitable for professionals.
- The interface is highly customizable.
- There is active community support and frequent updates.
- Cons:
- The learning curve is steep for beginners.
- There are occasional stability issues with certain distributions.
- The interface can appear cluttered for new users.
How to Install Kdenlive
- Ubuntu/Debian: Install via APT by running sudo apt install kdenlive. Alternatively, install the official PPA for the latest updates.
- Fedora: Use the command sudo dnf install kdenlive.
- Arch Linux: Install through the package manager with sudo pacman -S kdenlive.
- Flatpak: It is available on Flathub for distribution-independent installation.
Best for: Kdenlive is best suited to intermediate to professional video editors. These users require a robust, customizable tool with extensive features. Its active community support and regular updates make it ideal for users seeking a balance between ease of use and professional capabilities.
2. OpenShot
OpenShot is renowned for its simplicity and intuitive interface. It is one of the most suitable choices for beginners entering video editing on Linux.
The design is clean and user-friendly. You can quickly grasp the basics of video editing without feeling overwhelmed by complex features.
Despite its simplicity, OpenShot does not compromise functionality. It supports unlimited tracks and drag-and-drop editing.
It offers a variety of transitions, effects, and keyframe animations. These features add creative flair to your projects.
OpenShot supports a wide array of video formats. Import and export processes are smooth.
Due to its open-source nature, it encourages community contributions. It is updated frequently and new features are added on a regular basis.
It is ideal for hobbyists, educators, and content creators. OpenShot provides essential tools for everyday editing tasks. It also offers room to grow as your skills develop.
OpenShot Features
- Drag-and-drop editing: Simplify your workflow with an intuitive interface.
- Unlimited Tracks: Create complex projects with multiple layers.
- Keyframe Animations: Add dynamic effects to video transitions.
- Wide Format Support: Works with various video and audio formats.
- Built-In Transitions & Effects: Easily incorporate creative visual effects.
OpenShot Pros and cons
- Pros:
- It is extremely beginner-friendly.
- The interface is clean and straightforward.
- There are abundant online tutorials and community support.
- It is free and open source.
- Cons:
- It has limited advanced features compared to professional-grade editors.
- Performance may lag on large projects.
- Users report occasional minor bugs.
How to Install OpenShot
- Ubuntu/Debian: Install using APT with sudo apt install openshot-qt.
- Fedora: Use the command sudo dnf install openshot-qt.
- Arch Linux: It is available from the AUR.
- Snap/Flatpak: OpenShot can be installed from the Snap Store or Flathub for easier distribution and management.
Best for: OpenShot is suitable for beginners and casual users. It provides a straightforward, no-fuss video editing tool. Its simplicity and essential features make it suitable for educational purposes, home video projects, and quick edits of social media content.
3. Shotcut
Shotcut stands out as a versatile, open-source video editor. It strikes a balance between professional-grade features and ease of use. Software is designed modularly. Shotcut offers a native timeline for real-time editing.
It is a powerful tool even for demanding projects. Shotcut supports a wide range of audio and video formats.
This ensures compatibility with virtually any media you work with. Its extensive filter library includes advanced options.
These options cover color grading, transitions, and special effects. They enhance your videos with professional polish.
Shotcut’s performance is noteworthy. It optimizes system resources to provide a smooth editing experience.
This holds true even on mid-range hardware. An active development community ensures regular updates.
The intuitive yet customizable layout makes Shotcut accessible. It is ideal for users who want both simplicity and depth.
Shotcut Features
- Native Timeline Editing: Enjoy real-time previews and smooth editing.
- Advanced Filters and Effects: Use an extensive library for color grading, transitions, and more.
- Wide Format Support: It supports hundreds of audio and video formats.
- Modular Interface: Customize the layout to fit your workflow.
- Optimized Performance: It efficiently manages system resources even on mid-range hardware.
Shotcut Pros and cons
- Pros:
- It offers high performance and stability.
- There are extensive built-in filters and effects.
- Regular updates are driven by an active community.
- The interface is flexible and modular.
- Cons:
- The interface may be less intuitive for absolute beginners.
- It requires time to master the advanced features.
- There are fewer tutorials available than some competitors.
How to Install Shotcut
- Ubuntu/Debian: Install via APT or download the AppImage from the Shotcut website.
- Fedora: It is available in the official repositories using the sudo dnf install shotcut.
- Arch Linux: Install via the package manager with sudo pacman -S shotcut.
- Flatpak: Download from Flathub for easy installation.
Best for: Shotcut is ideal for intermediate users. It is a powerful yet approachable video editing tool. It benefits users with moderate to advanced editing needs. They appreciate extensive format support and built-in filters and effects.
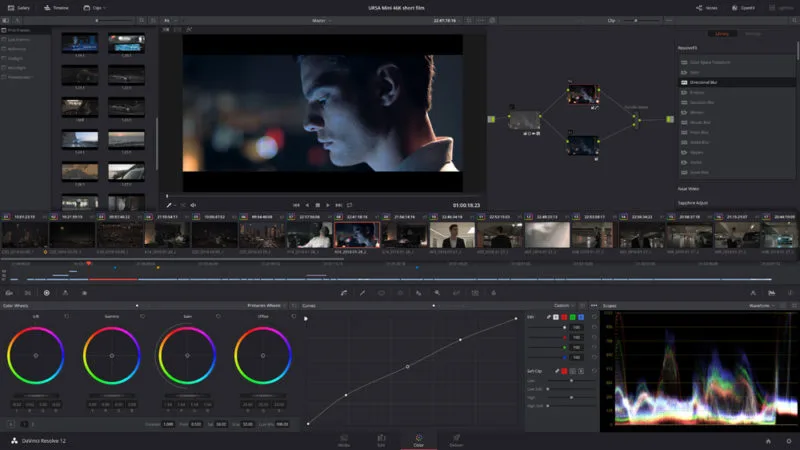
4. DaVinci Resolve for Linux
DaVinci Resolve is the industry standard for professional video editing and color correction. It is now available on Linux. This powerful software integrates an advanced suite of tools.
It caters for every aspect of post-production. These aspects include cutting, editing, sophisticated color grading, and audio mixing.
DaVinci Resolve’s interface is efficient. It features a timeline that accommodates multi-track editing.
It also uses a node-based system for complex visual effects. Its color grading tools are unparalleled. They offer precise control over every detail. This ensures cinematic quality.
The inclusion of the Fusion module provides advanced compositing. It is ideal for sophisticated visual effects. DaVinci Resolve demands robust hardware.
You need a high-performance GPU, ample RAM, and a modern processor. The results justify this investment for filmmakers and professional content creators.
Constant updates and refinements keep it on the cutting edge. It is a top choice for Linux professionals.
DaVinci Resolve Features
- Advanced Color Grading: Precise tools help you achieve cinematic visuals.
- Fusion Module: A node-based system that enables sophisticated visual effects.
- Comprehensive Audio Post-Production: Integrated tools edit and mix audio.
- Multi-track editing: Manage complex projects easily.
- Professional Interface: Designed for efficient workflows and high-end production.
DaVinci Resolve Pros and cons
- Pros:
- It offers industry-standard, professional-grade editing features.
- Color grading and visual effects tools are unparalleled.
- It has a robust toolset for comprehensive post-production.
- It is widely used in the film and broadcast industry.
- Cons:
- It has high system requirements that necessitate powerful hardware.
- New users face a steep learning curve.
- Linux installation and setup can be complex.
- It is not ideal for casual or quick edits.
How to Install DaVinci Resolve
- Official Installer: Download the latest Linux version from the Blackmagic Design website.
- Dependencies: Ensure your system has the required GPU drivers and libraries installed.
- Installation: Follow the provided installation script and detailed setup instructions for your specific Linux distribution.
Best For: DaVinci Resolve is suitable for professional video editors and filmmakers. They require advanced color grading, visual effects, and audio editing capabilities. It is ideal for high-end hardware users. They want to produce broadcast-quality and cinematic projects.
5. Blender (Video Sequence Editor – VSE)
Blender is a multifaceted tool. It is known for its 3D modeling and animation capabilities. However, its Video Sequence Editor (VSE) is incredibly powerful for video editing.
Blender’s VSE allows non-linear editing. You can cut, splice, and arrange clips precisely.
Blender uniquely integrates 3D animation with traditional video editing. This provides an all-in-one solution.
It is suitable for projects that require both visual effects and conventional editing. Blender offers a comprehensive suite of tools. These include transitions, filters, and composite capabilities.
It is a versatile option for creative professionals. Although Blender has a steep learning curve, there are many tutorials available. An active community eases the process.
Whether you are crafting a short video or an elaborate animated film, Blender’s VSE is robust. It helps you achieve professional-quality results while embracing open-source.
Blender Features
- Non-linear editing: Enjoy a flexible timeline for precise clip management.
- Integrated 3D & Compositing: Combine 3D animations with video editing seamlessly.
- Extensive Toolset: Access a wide range of transitions, filters, and effects.
- Customizable Interface: Adapt the workspace to your editing style.
- Advanced Rendering: Leverage Blender’s renowned rendering engine for high-quality outputs.
Blender Pros and cons
- Pros:
- It is a versatile, all-in-one solution for video and 3D editing.
- It is completely free and open source.
- There is extensive community support and many tutorials.
- It is highly customizable and powerful when mastered.
- Cons:
- It has a steep learning curve for new users.
- The interface can be overwhelming compared to dedicated video editors.
- Video editing functionality may not be as refined as specialized software.
How to Install Blender
- Ubuntu/Debian: Install via APT with sudo apt install blender or download the latest version from the Blender website.
- Fedora: Use the command sudo dnf install blender.
- Arch Linux: Install via sudo pacman -S blender.
- Snap/Flatpak: Blender is available on both the Snap Store and Flathub for distribution-independent installation.
Best For: Blender’s VSE is suitable for creators who want an all-in-one solution. They require both video editing and 3D animation. It is ideal for projects that require traditional editing and advanced visual effects. This makes it a powerful tool for experimental and multimedia art projects.
Other Noteworthy Linux Video Editing Tools
Lightworks
Lightworks provides a professional-grade editing suite. It offers a free version that packs many advanced features.
Although its premium version unlocks additional capabilities, the free edition is robust. It offers trimming, timeline editing, and a range of effects that cater to filmmakers on a budget.
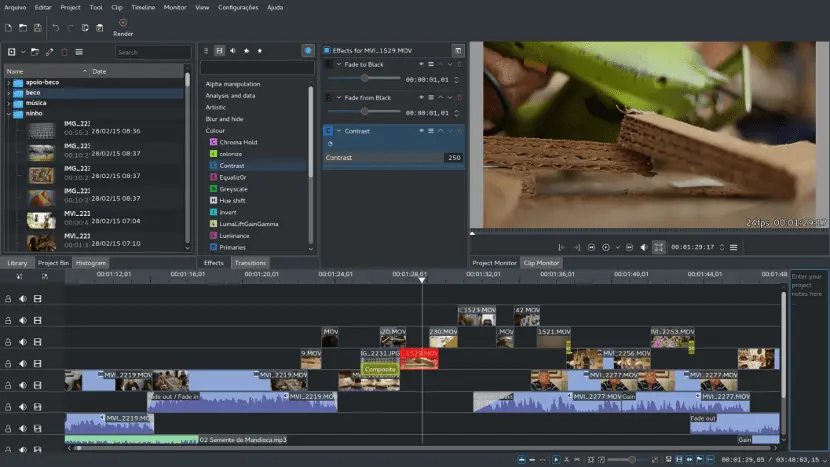
Cinelerra
Cinelerra has a long-standing reputation. It was one of Linux’s earliest video editors. It is known for its stability and extensive feature set.
Although its interface may appear complex, it is highly capable. It is ideal for users who demand precise control over their editing workflow.
Pitivi
Pitivi is designed for simplicity. It offers a minimalist interface that makes video editing accessible to beginners.
Its streamlined workflow is perfect for users who need to edit videos quickly. It does this without a steep learning curve. It still maintains enough features for more detailed projects.
Comparison Table
Here is a comparison table of the best Linux video editing software, with key features, best for and install. This table will help you choose the best software for your video editing needs.
| Software | Best For | Key Features | Installation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kdenlive | Intermediate to Professional Editors | Multi-track editing, customizable interface, proxy editing, extensive effects | APT, DNF, Pacman, Flatpak, Official PPA |
| OpenShot | Beginners and Casual Users | Drag-and-drop editing, unlimited tracks, keyframe animations, built-in transitions | APT, DNF, AUR, Snap, Flatpak |
| Shotcut | Intermediate Users | Native timeline editing, advanced filters, modular layout, wide format support | APT, DNF, Pacman, AppImage, Flatpak |
| DaVinci Resolve | Professional Editors and Filmmakers | Advanced color grading, Fusion module, comprehensive audio post-production | Official Installer from Blackmagic Design, Dependencies |
| Blender (VSE) | Multimedia Artists (Video + 3D) | Integrated 3D modeling and video editing, non-linear editing, extensive toolset | APT, DNF, Pacman, Snap, Flatpak |
| Lightworks | Budget-Conscious Professionals | Advanced trimming, timeline editing, professional-grade effects | APT, Official Installer, Third-Party Repositories |
| Cinelerra | Experienced Editors Seeking Precision | Detailed timeline, real-time editing, robust effects, high stability | Download from Official Website, Package Repositories |
| Pitivi | Beginners and Hobbyists | Minimalist design, efficient workflow, easy-to-use interface | APT, DNF, Snap, Flatpak |
How to Choose the Right Software for Your Needs
Choosing the most suitable video editor for Linux requires you to balance creative ambitions and practical considerations.
You must consider hardware capabilities and ease of use. Determine whether you need basic editing tools for quick projects or advanced features for professional-grade work.
Assess your system’s CPU, GPU, and memory. High-end tools like DaVinci Resolve demand powerful hardware.
Lightweight editors like OpenShot or Pitivi run well on older systems. Evaluate the learning curve associated with each software.
A tool with a simple, intuitive interface might be preferable if you are new to video editing. Consider tutorials, forums, and regular updates.
A vibrant community can enhance your learning process. It can also help resolve technical issues.
Finally, opt for software that updates frequently. This ensures you have access to the latest features and security updates.
Tips and Tricks for Optimizing Your Linux Video Editing Workflow
Improving your workflow is crucial to productivity and creativity. Here are some practical tips.
Optimize system performance
- Regular maintenance: Update your Linux distribution and drivers. This ensures optimal performance.
- Resource Management: Close unnecessary applications during editing. This frees up system resources.
- SSD Storage: Use SSDs for your project files. This reduces load times and improves rendering speeds.
Customize Your Editing Environment
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Learn and customize shortcuts. This speeds up your workflow.
- Workspace Layouts: Tailor your interface by rearranging panels. Save custom layouts for different editing tasks.
- Templates and Presets: Utilize built-in templates for recurring tasks. This streamlines your process.
Troubleshooting and backup
- Frequent Backups: Use the autosave feature. Backup your projects regularly to avoid data loss.
- Proxy Files: Create proxy files for high-resolution footage. This ensures smooth editing.
- Community Support: Engage in online forums. They offer troubleshooting tips and best practices.
Advanced Editing Techniques on Linux
For those looking to elevate their video editing skills, mastering advanced techniques is key. These techniques can transform your projects into professional masterpieces.
Color Correction and Grading
- Precision Tools: Use histograms, waveforms, and LUTs. These tools help you adjust color balance.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Many editors provide live preview tools. You can see the adjustments instantly.
Integrating Special Effects
- Motion Graphics: Utilize integrated 3D capabilities. Blender provides these, or use dedicated modules like Fusion in DaVinci Resolve.
- Layered Overlays: Enhance storytelling with text overlays. Use lower-thirds and graphics for added effect.
Audio enhancement
- Audio Sync: Ensure your audio tracks align perfectly with your video timeline.
- Mixing and Effects: Apply noise reduction, equalization, and sound effects. This creates a rich auditory experience.
Future Trends in Linux Video Editing
Linux video editing software is evolving rapidly. New technologies and community-driven innovations are emerging.
Artificial intelligence and automation
- Smart Editing: Future versions may include AI-powered scene detection. They might also offer automated cuts and smart color grading.
- Efficiency Gains: Automation tools reduce manual editing time. This lets you focus more on the creative aspects.
Community-driven development
- Open-Source Collaboration: More developers contribute. Expect continuous improvements and innovative features.
- Custom Extensions: User-generated plugins and extensions further customize the editing experience.
Conclusion
Linux video editing software allows you to express your creative vision without having to worry about expensive licenses or restrictive systems.
Whether you’re a beginner learning the basics or a professional seeking advanced features, Kdenlive, OpenShot, Shotcut, DaVinci Resolve, and Blender provide the perfect solution for any project.
As Linux is an open-source operating system, you have the freedom to explore, experiment, and refine your craft without any limitations.
It offers stable, secure, and dynamic environments that adapt to your creative needs while delivering high-quality results.
As with Windows, Linux is also capable of meeting your needs, whether you are editing social media or producing full-scale films.
Linux video editing software not only allows you to save money, but it also allows you to join an active community that continually enhances and improves the technology.
Discover a world of possibilities where your imagination is the only limit. Engage your creativity, unleash your imagination, and discover the world of possibilities.
Now is the time for you to explore, create, and let your vision shine through Linux video editing.
Frequently Asked Question
Which Linux video editor is best for complete beginners?
OpenShot is an excellent starting point for beginners. Its interface is intuitive and easy to learn, which makes it accessible for those new to video editing. The software uses drag-and-drop functionality to simplify the editing process. Additionally, there are many online tutorials available. These resources make learning video editing easier and help you master the basics quickly.
Can DaVinci Resolve run on most Linux distributions?
DaVinci Resolve requires a modern, high-performance Linux distribution to run effectively. It also depends on a robust GPU to manage its advanced features. Always review the official system requirements before installation. This ensures compatibility with your hardware and prevents performance issues. Checking these requirements in advance helps you avoid unexpected problems during the editing process.
What hardware is recommended for professional-grade video editing on Linux?
For demanding video editing projects, it is essential to use powerful hardware. A high-performance CPU is necessary to handle complex editing tasks. You should also have at least 16GB of RAM to ensure smooth performance. Additionally, a high-performance GPU improves rendering speeds and video playback. Using SSD storage is also highly recommended. This ensures faster data access and enhances overall editing efficiency.
Are Linux video editors as powerful as those on Windows or macOS?
Absolutely. Open-source editors like Kdenlive, Shotcut, and DaVinci Resolve offer robust features and advanced capabilities. These tools are comparable to their Windows and macOS counterparts in terms of functionality. In addition to their power, Linux video editors also provide greater customization. This flexibility allows you to tailor the software to your specific needs while saving costs.
How frequently do Linux video editing tools receive updates?
Popular Linux video editors receive frequent updates to maintain and improve their functionality. Active communities ensure that these updates deliver new features and enhancements regularly. Security patches are also provided to keep your editing environment safe and reliable. This consistent development keeps the software current. It also ensures that you have access to the latest advancements in video editing technology.